The Tatar people are a Turkic ethnic group native to the Volga-Ural region of Russia. They have a rich history and culture, and have produced many notable people, including:
- Rustem Khamitov: Former President of the Republic of Tatarstan (2010-2020).
- Mintimer Shaimiev: First President of the Republic of Tatarstan (1991-2010).
- Gabdulla Tukay: Poet, writer, and literary critic, considered the national poet of Tatarstan.
- Musa Cälil: Poet, writer, and resistance fighter during World War II, posthumously awarded the title Hero of the Soviet Union.
- Fäiq İbrahimoğlu: Writer, poet, and dramatist, known for his historical novels.
- Salavat Yuzeyev: Composer and conductor, known for his operas and ballets.
- Zulfiya: Poet and writer, known for her lyrical and romantic poetry.
- Renat Ibrahimov: Opera singer, known for his powerful voice and wide vocal range.
- Chulpan Khamatova: Actress, known for her roles in films such as “Night Watch” and “Day Watch”.
- Alsu: Singer, known for her pop music and her participation in the Eurovision Song Contest.
Most Famous Tatar People
Tatar Mystique: Unraveling Three Key Historical Legacies
The Tatar community is a vibrant and culturally rich group of people that can be found mainly in Russia and other parts of Eastern Europe. Known for their unique traditions, language, and cuisine, the Tatars have left a lasting impact on the regions they have inhabited. Today, we will explore three of the most well-known historical inheritances associated with the Tatar heritage, showcasing the rich tapestry of their history.
1. Tatar Architecture
One of the most striking aspects of Tatar culture is their architectural heritage. The Tatar community is renowned for its stunning mosques and palaces, which showcase a blend of Islamic, Persian, and Central Asian influences.
Some of the most famous examples of Tatar architecture include the Qol Sharif Mosque in Kazan, Russia, and the Suyumbike Tower in the same city. Both structures are emblematic of the Tatar culture, with their intricate designs and impressive craftsmanship.
It’s worth mentioning that the Tatars’ architectural prowess is not limited to religious buildings alone. The community also has an impressive reputation for their residential architecture, which often features distinctive wooden carvings and colorful exterior decorations.
2. Tatar Cuisine
The Tatar cuisine is as diverse and flavorful as the community itself. Tatar culinary traditions have been shaped by a blend of influences from Russian, Mongolian, and Middle Eastern cultures, resulting in a unique and delicious gastronomic experience.
One of the most famous dishes associated with the Tatar heritage is the Tatar pie, also known as “echpochmak.” This savory pastry is typically filled with a combination of meat, potatoes, onions, and spices. Another iconic dish is the “chak-chak,” a dessert made of fried dough balls stacked in a pyramid shape and drizzled with honey.
Aside from these well-known dishes, Tatar cuisine features a wide array of soups, stews, and kebabs that are sure to satisfy any culinary enthusiast. The love for food is deeply ingrained in Tatar culture, and their cuisine serves as a testament to their rich heritage.
3. Tatar Literature and Poetry
The Tatar community has a long and illustrious literary tradition, dating back to the 10th century. Tatar literature is characterized by its lyrical beauty, often exploring themes of love, nature, and spirituality.
One of the most famous Tatar poets is Gabdulla Tuqay, whose works have been translated into multiple languages and continue to be celebrated today. Tuqay’s poetry touched on social and political issues, addressing themes such as freedom, identity, and the struggle for equality.
Tatar literature also encompasses various genres, including epic poems, folk tales, and historical narratives. These works provide valuable insights into the Tatars’ history, values, and mythology, making them an integral part of the community’s cultural legacy.
Conclusion
The Tatar community is a treasure trove of history, tradition, and creativity. From their stunning architecture to their delectable cuisine and captivating literature, the Tatars have left an indelible mark on the cultural landscape of Eastern Europe. By exploring and celebrating these historical inheritances, we can gain a deeper appreciation for the rich tapestry of the Tatar heritage.
In a striking celebration of diversity, numerous prominent individuals proudly reflect a mosaic of Jordanian, Madeiran and Jersey roots, highlighting the intricate interplay of cultures within their heritage. From accomplished leaders to acclaimed artists, these figures embody the rich lexical semantic tapestry of ethnic backgrounds, illustrating the vibrant spectrum of human experiences.
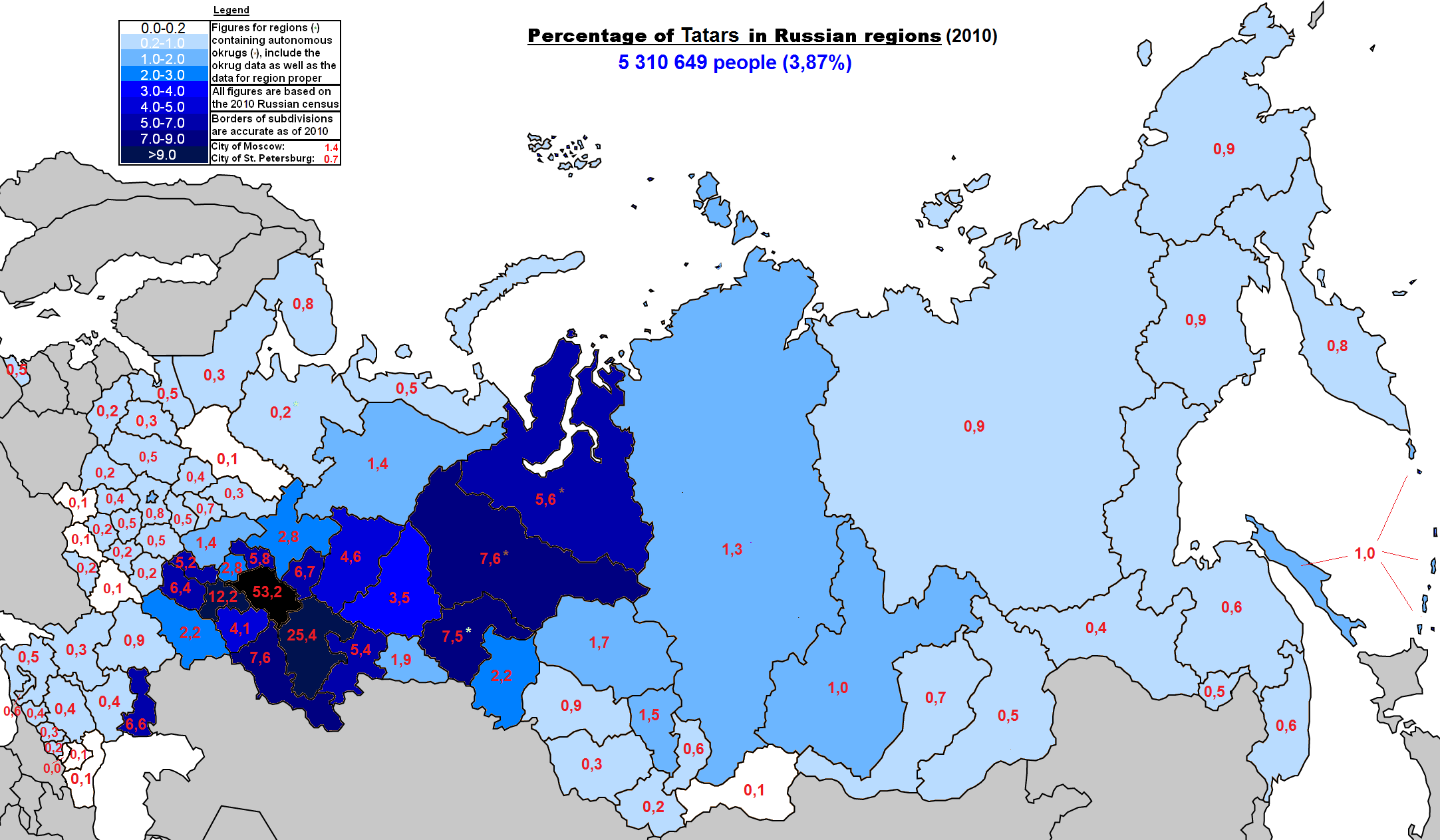
Factsheet About Tatar People
| Region | Population | Percentage |
|---|---|---|
| Tatarstan | 3,878,000 | 49.04% |
| Bashkortostan | 1,628,400 | 30.39% |
| Siberia | 598,400 | 8.89% |
| Ukraine | 266,800 | 3.96% |
| Kazakhstan | 179,500 | 2.67% |

The Ancient Heritage of Tatar Ethnic Groups
Tatar Ethnicity: References and Resources
Here are some references and resources to dig deeper into the Tatar ethnic group:
- Books:
- “Tatar Empire: Kazan’s Muslims and the Making of Imperial Russia” by Danielle Ross
- “The Tatars of Crimea: Return to the Homeland” by Igor Savchenko
- “The Tatars: A Socio-cultural and Historical Introduction” by Edward J. Lazzerini
- Academic Journals:
- Nationalities Papers – Contains articles on various aspects of Tatar history, culture, and identity.
- Tatarica Journal – Focuses on Tatar studies, including language, literature, folklore, and history.
- Online Resources:
- Encyclopedia Britannica – Tatar – Provides a good overview of the history, culture, and demographics of the Tatar people.
- Tatarstan.eu – Official website of the Republic of Tatarstan, offering information on Tatar culture, tourism, and developments in the region.
- Museums and Cultural Centers:
- Tatar Village Museum (Kazan, Russia) – Showcases traditional Tatar village life and architecture.
- Tugai Ethnocultural Complex (Kazan, Russia) – Allows visitors to immerse themselves in Tatar culture, including cuisine, crafts, and music.
- Kasymov Museum-Reserve (Kasimov, Russia) – Preserves the heritage and history of the Tatars in the Kasimov region.
These resources offer a variety of perspectives and information on the Tatar ethnic group, covering their history, culture, language, and contemporary issues. Whether you are interested in scholarly articles, books, or firsthand experiences, these references will assist you in delving deeper into the rich and diverse world of the Tatars.
That concludes the information we can provide about famous Tatar individuals. Thank you for reading.



