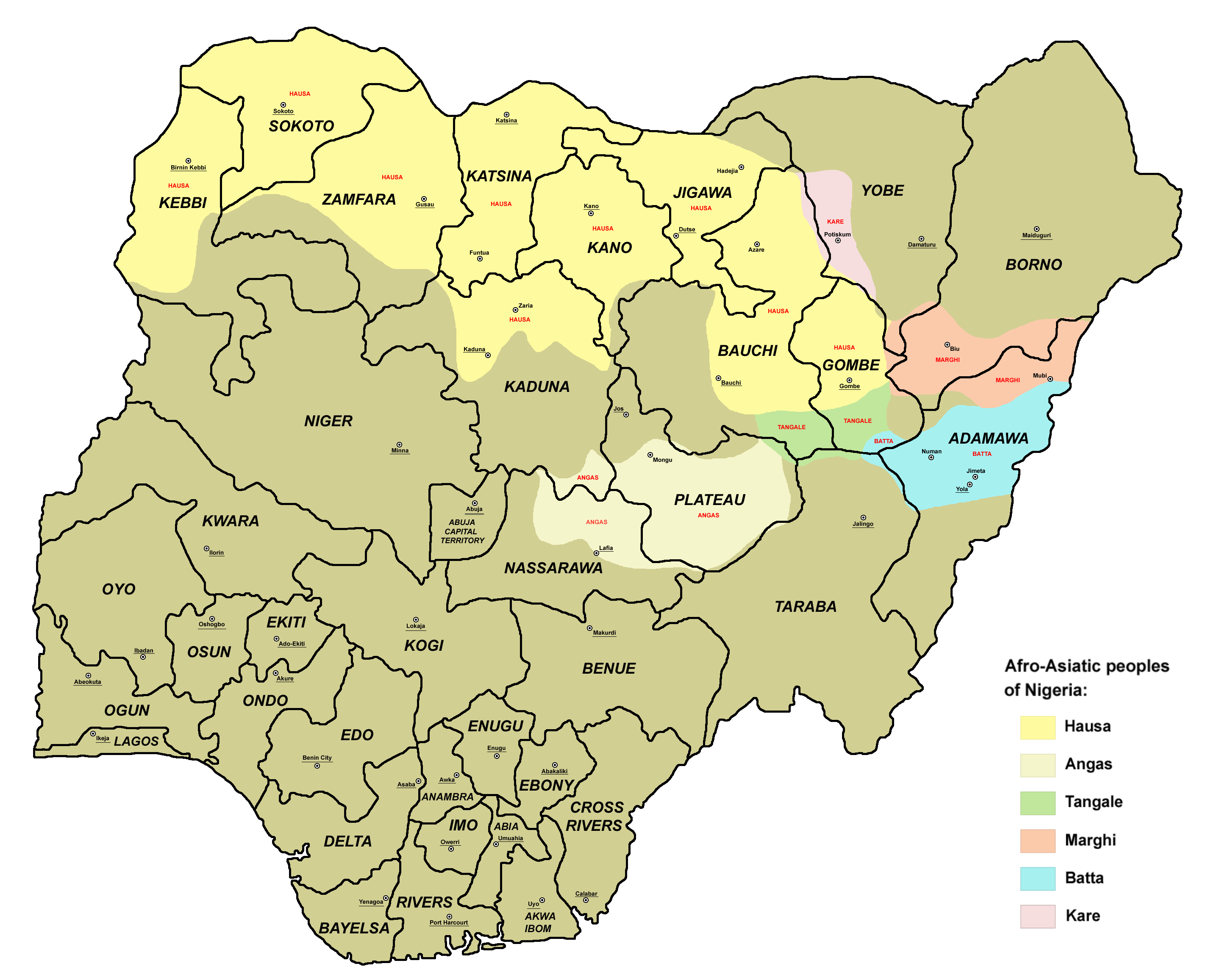
The Hausa people, with a vibrant history and culture, are an ethnic group primarily concentrated in northern Nigeria, southern Niger, eastern Burkina Faso, and western Cameroon. They can be found in many other parts of Africa as well. This ethnic group has produced numerous prominent individuals who have made significant contributions to various fields.
- Aminu Kano: (1920-1983) A prominent Nigerian politician, educationist, and trade unionist, Aminu Kano was a founding member of the Northern Elements Progressive Union (NEPU) and a strong advocate for social justice and education.
- Ahmadu Bello: (1910-1966) The first Premier of Northern Nigeria, Ahmadu Bello played a crucial role in the country’s independence movement and served as the President of the Northern People’s Congress (NPC).
- Ibrahim Babangida: (Born 1941) A former military ruler of Nigeria, Ibrahim Babangida served as the country’s President from 1985 to 1993. He is known for introducing significant economic and political reforms during his tenure.
- Abubakar Tafawa Balewa: (1912-1966) Nigeria’s first Prime Minister, Abubakar Tafawa Balewa, played a pivotal role in the country’s independence struggle and served as the leader of the NPC.
- Hadiza Bala Usman: (Born 1976) A Nigerian activist and development expert, Hadiza Bala Usman served as the Managing Director of the Nigerian Ports Authority and was instrumental in promoting transparency and efficiency in the maritime sector.
- Aisha Jummai Al-Hassan: (1959-2021) A Nigerian politician, Aisha Jummai Al-Hassan served as the first elected female governor of Taraba State. She was known for her commitment to education and gender equality.
- Nuradeen Abdullahi: (Born 1966) A renowned Nigerian poet, playwright, and novelist, Nuradeen Abdullahi writes in Hausa and has won numerous awards, including the prestigious Noma Award for Publishing in Africa.
- Mukhtar Ramalan Yero: (Born 1968) A Nigerian politician, Mukhtar Ramalan Yero served as the Governor of Kaduna State and was known for his emphasis on education and infrastructural development.
- Sanusi Lamido Sanusi: (Born 1961) A Nigerian economist and former Governor of the Central Bank of Nigeria, Sanusi Lamido Sanusi is known for his outspoken stance on economic issues and his commitment to transparency and accountability.
- Ali Nuhu: (Born 1974) A Hausa actor, Ali Nuhu is one of the most popular and successful actors in the Nigerian film industry, known for his charismatic performances and leading roles in numerous movies.
Most Famous Hausa People
Hausa Mystique: Unraveling Three Key Historical Legacies
The Hausa ethnic group is one of the largest in Africa, primarily found in Nigeria, Niger, and other West African countries. With a rich and diverse cultural heritage, the Hausa community has made lasting contributions in various fields. Here are three of the most well-known historical inheritances associated with the Hausa heritage:
- The Hausa Language: One of the most noticeable aspects of the Hausa community is their language. Hausa is spoken by over 50 million people, making it one of the most widely spoken languages in Africa. It is an Afro-Asiatic language, belonging to the Chadic subfamily. The Hausa language has a rich literary tradition, with written works dating back several centuries. It is also used extensively in trade, commerce, and communication across West Africa, making it an important lingua franca in the region.
- Hausa Architecture: The Hausa people are known for their distinctive architectural style, which is characterized by intricate details, unique designs, and vibrant colors. Hausa architecture is influenced by both Islamic and traditional African styles. One prominent example of Hausa architecture is the traditional mud-brick houses known as “compounds.” These compounds often feature courtyards, multiple rooms, and decorative elements such as carved wooden doors and intricate patterns on the walls. This architectural style can be seen not only in residential buildings but also in religious structures such as mosques.
- Hausa Traditional Attire: The Hausa community is renowned for their vibrant and elegant traditional attire. One of the most iconic Hausa outfits is the flowing gown known as “boubou” or “babban riga” for men and “m’lahfa” for women. These gowns are often made from colorful and patterned fabrics, with intricate embroidery and embellishments. The embroidery work, known as “zari,” is a significant part of Hausa traditional attire, with artisans using gold or silver threads to create intricate patterns. Hausa traditional attire reflects the cultural pride and sense of identity among the community.
These are just a few examples of the historical inheritances associated with the Hausa heritage. The Hausa community’s language, architecture, and traditional attire are not only significant aspects of their cultural identity, but they also contribute to the rich heritage of West Africa.
In a striking celebration of diversity, numerous prominent individuals proudly reflect a mosaic of Choa, Biu Mandara and Mbam roots, highlighting the intricate interplay of cultures within their heritage. From accomplished leaders to acclaimed artists, these figures embody the rich lexical semantic tapestry of ethnic backgrounds, illustrating the vibrant spectrum of human experiences.
Factsheet About Hausa People
| Country | Population | Percentage |
|---|---|---|
| Nigeria | 39,022,966 | 19% |
| Niger | 7,802,365 | 55% |
| Ghana | 683,656 | 2% |
| Benin | 511,456 | 4% |
| Togo | 244,596 | 2% |
| Cameroon | 114,725 | 0.5% |
The Ancient Heritage of Hausa Ethnic Groups
References to the Hausa Ethnic Group
The Hausa ethnic group is one of the largest ethnic groups in Africa, with a population of over 70 million people. They are predominantly located in Nigeria, Niger, and several other West African countries. If you are interested in learning more about the Hausa people, here are some references and resources to help you dig deeper:
- “The Hausa of Nigeria: An African Society in the Making” by Paul E. Lovejoy: This book provides a comprehensive overview of the Hausa people’s history, culture, and society. It explores their pre-colonial, colonial, and post-colonial experiences, as well as their economic, political, and religious systems.
- “Hausaland Divided: Colonialism and Independence in Nigeria and Niger” by David Robinson: This book delves into the effects of colonialism on the Hausa people in both Nigeria and Niger. It examines the social, economic, and political changes that occurred during and after the colonial period, shedding light on the challenges faced by the Hausa community.
- “A History of the Hausa People” by Abdulqadir Mukhtar: This book offers a detailed historical perspective on the Hausa people, tracing their origins and development over centuries. It covers topics such as their ancient civilizations, interactions with other ethnic groups, and the rise and fall of Hausa empires.
In addition to these books, there are several online resources that provide valuable insights into the Hausa ethnic group:
- HausaDictionary.com: This website offers an extensive Hausa dictionary, allowing you to explore the Hausa language and learn common words and phrases. It also provides information on Hausa culture, proverbs, and folktales.
- “The Hausa: Culture, Customs, Traditions, and their Role in Nigeria” (a research article by Raimi Rufus Lanre): This article provides a comprehensive overview of the Hausa culture, customs, and traditions. It explores important aspects such as their language, religion, family structure, dress, and food.
- “The Hausa Ethnic Group: Origin, Language, Culture, Traditional Attires, Food and Lifestyle” (an article by Nigerian Finder): This article offers a general introduction to the Hausa ethnic group, highlighting key aspects of their history, language, culture, and traditional practices. It also provides insights into their traditional attires, food, and lifestyle.
By exploring these references and resources, you will gain a deeper understanding of the Hausa ethnic group, their rich cultural heritage, and their significant contributions to the diverse tapestry of Africa.
That concludes the information we can provide about famous Hausa individuals. Thank you for reading.




![The Khmer people (Khmer: ជនជាតិខ្មែរ, Chônchéatĕ Khmêr [cɔnciət kʰmae]) are an Austroasiatic ethnic group native to Cambodia. They comprise over 90% of Cambodia's population of 17 million. They speak the Khmer language, which is part of the larger Austroasiatic-language family alongside Mon and Vietnamese.
The majority of the Khmers follow Theravada Buddhism. Significant populations of Khmers reside in adjacent areas of Thailand (Northern Khmer) and the Mekong Delta region of neighboring Vietnam (Khmer Krom), while there are over one million Khmers in the Khmer diaspora living mainly in France, the United States, and Australia.](https://upload.wikimedia.org/wikipedia/commons/3/37/Khmer_Robam_Apsara_%28cropped%29.png)